Keto Diet - How Many Carbs are on Keto Diet

Carbs on Keto: 3 Steps to Determine Your Personal Macros
Introduction to the Ketogenic diet
Low-carbohydrate diets have been all the rage for years. Carbohydrate restriction is a well-known way to reduce total calorie intake, balance blood sugar, and reduce body weight.
What makes the keto diet different is that the diet not only requires extremely low net-carb intake but very high-fat content.
While the carb counts are generally recommended to be somewhere between 20 and 50 grams of net carbs per day, your optimal target won’t be the same as everyone else's.
Factors that affect your target carb intake include your body weight, body fat percent, fitness level, and baseline caloric needs.

But wait, isn't fat bad for you?
For a couple of generations, we have been told that dietary fat is the culprit of a whole list of ailments including higher rates of obesity, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease.
But today, this low-carb and high-fat diet has been clinically proven to actually improve these conditions by promoting effective and significant weight loss (Source).

How the ketogenic diet works
In a typical modern diet, the majority of our calories come in the form of carbohydrates, with moderate protein intake and a little bit of dietary fat. This is a matter of efficiency, as high-carb foods are easy to process into immediate energy in the form of glucose (sugar).
The keto diet reduces carbohydrate consumption but also has numerous health benefits.
Generally, a person who eats much lower carbs will burn fat as a fuel source. Your liver converts fat to energy molecules called ketones, which are used by the brain to produce energy.
Eating keto diets can significantly lower blood glucose and help reduce fat storage. Numerous studies show weight loss with keto without counting calories. Keto diets are also good at decreasing blood sugars as well as improving blood pressure.
The keto diet works by robbing the body of glucose by dramatically restricting carbohydrate intake.
When the body runs out of this convenient form of energy, it burns fat instead, turning it into a form of energy called ketone bodies. When the body is mostly running on ketones, it is in a metabolic state called "ketosis".

How to achieve ketosis
Ketosis occurs naturally in the event of starvation or fasting.
Insulin levels drop and stored fat becomes the body's primary energy source. Ketosis is therefore a preferred metabolic state when calories are restricted because your fat stores break down instead of your lean body mass.
Ketogenic diets promote nutritional ketosis.
A very low carbohydrate diet deprives the metabolism of glucose, keeping ketone levels high without requiring starvation.
Macronutrients
You can follow the keto diet by establishing a daily carb limit. Eat keto by restricting foods with high net carbs and fueling up on healthy fats and protein. You keep track of your nutrition by counting macros.
What are macros?
While micronutrients are all the vitamins and minerals that are essential nutrients for our bodies to build and repair, macronutrients are the foods that give your body energy.
There are three forms of macronutrients:
Fats
On the ketogenic diet, healthy fats are your best friends. You get 9 calories for every gram of fat.
Examples of healthy fats include plant fats–like olive oil and coconut oil–as well as fatty foods like avocados and animal protein such as butter, ghee, and lard.
What’s MCT oil?
Medium Chain Triglycerides (or MCTs) are a form of saturated fat that is able to skip primary digestion and go straight to the liver, where they break down into ketone bodies. They do this whether you’re in ketosis or not.
MCT supplements can help give you the energy boost you would normally turn to carbs for, while also enhancing the benefits of ketosis.

Protein
Protein does not necessarily throw you out of ketosis, but it doesn’t turn into ketones.
You get 4 calories for every gram of protein.
Eat plenty of protein to get your needed calories.
Just keep in mind that the more calories that come from protein, the fewer ketones make it into your blood.
Examples of what is keto diet friendly, quality protein include nuts, seeds, eggs, fresh meat, and seafood.
Carbohydrates
On a typical, non-restricted diet, carbohydrates make up the majority of consumed calories.
On the keto diet, we go to great lengths to restrict the number of net carbs consumed each day.
You get 9 calories for every gram of carbohydrate, but the story doesn’t end there.

Net carbs
Net carbs are calculated by taking the total carbs minus fiber and sugar alcohols.
Fiber, though vital to our digestive health, does not provide calories when eaten. Likewise, sugar alcohols are difficult for the body to digest and do not cause changes in blood sugar levels.
Because of this, most keto diets subtract both fiber and sugar alcohols from total carbs and aim for net carbs per day.
For example, a food may have 15 grams of carbs and 6 grams of fiber–this would mean you only have to record 9 grams of net carbs.
This approach to counting net carbohydrates is important because it makes it possible to include fruits and veggies that might seem to be too high in carbs at first glance.
Low-carb veggies include non-starchy vegetables like leafy greens, cucumbers, broccoli, cauliflower, asparagus, and squash.
Want to make your food choices easy? Check out Kevin’s selection of meal kits and recipes!
This mild but flavorful curry will make a great meal for the entire family! Tender chicken breast strips in a rich and creamy blend of coconut milk, basil and Thai spices.
Thai-style coconut chicken
How to Determine Your Personal Macros
Step 1: Pick your Keto Diet
Before you embark on your keto journey, it’s important you understand that there are several variations of the keto diet.
Each version has different recommendations for the proportions of fat, protein, and carbs you should aim for each day.
The best approach to keto varies depending on what your goal is.
- The Standard Ketogenic Diet (SKD): The standard ketogenic diet is the form of the diet that most dieters are familiar with. It’s very low-carb, moderate-protein, and high in fat. Your macros stay the same every day. When following the SKD you should aim for no more than 5-10% of your daily calories to come from carbs. Protein should be 15-20% and fat 70-75%.
- The Cyclical Ketogenic Diet (CKD): The cyclical ketogenic diet is a variation on the diet that allows your total carbohydrate intake to vary by the day. The CKD allows for 2 non-consecutive days of higher-carb intake, usually for the sake of athletic performance. By allowing you more carbs (100-150g) the day before an intense workout, your liver is able to store up that glucose and use it to enhance your performance. Keep in mind that 100-150g is still considered low-carb. It’s important that your total energy intake doesn’t exceed the number of calories you’re able to burn during on your carb-heavy days, as the goal is to use up all your glycogen and return to burning fat for fuel as soon as possible.
- The Targeted Ketogenic Diet (TKD): The Targeted ketogenic diet (TKD) is very similar in concept to the cyclical ketogenic diet. The difference is that higher carbohydrate foods are saved for right before workouts, rather than planning an entire day of consuming more carbs. This approach to the ketogenic diet has also been useful for neurological conditions such as narcolepsy and dementia. Ketosis improves cognitive function in these illnesses, and saving carb consumption for periods when it’s less critical to perform (such as before bed) can improve the quality of life for individuals with these crippling conditions.
- The High-Protein Ketogenic Diet (HPKD): The high-protein ketogenic diet is much like the standard keto diet in that you still stick to just 5-10% of your daily calories coming from carbohydrates. But instead of 15-20% of your calories coming from protein, you aim for 30% protein instead, reducing your fat intake to 60-65%. It may not sound like a huge change, but for some people this means double the protein each day!
The HPKD is still a high-fat, low-carb diet and will stabilize your blood sugar, increase your energy, and reduce your cravings. There are just two big differences:
- It’s much easier to implement, as consuming 70%+ of your calories in fat can be difficult.
- Ketosis is harder to get to and maintain. If you have too much protein in your diet, your glucose levels will get too high and your ketone levels will get too low to keep you in ketosis.
HPKD is a good option for men and bodybuilders who are used to eating a lot of protein and are likely to burn through any excess glucose that is generated (yes, protein turns into glucose too).
Want to kickstart your keto journey? Check out this Teriyaki-style Chicken:
Tender chicken breast strips in a sweet and savory teriyaki sauce made with coconut aminos, ginger, and garlic. Add some broccoli, carrots, and riced cauliflower to have a delicious chicken stir-fry bowl.
Teriyaki-style Chicken
Dirty Keto/Lazy Keto
This version of the keto diet keeps things simple.
Just keep your keto carb limit below 5-10% of your daily calories, and eat the rest of your calories in fat and protein.
This version of the diet may not get you all the way into ketosis, but your body still burns fat, and you will still lose weight as long as you don’t overdo it on calories.
This version of low-carb eating can be an excellent stepping stone into or out of a stricter form of the keto diet.
Whatever version of the diet you pick, remember that you’ll likely adjust and find a sweet spot just for you that might not fit any of these templates perfectly. That’s just fine! It’s a starting point.

Step 2: Calculate your Macros
Just like any other diet, you’ll want to consider your fat-loss goals before determining what your daily caloric needs are.
Even if you’re aiming for dramatic results, it’s hard to keep to a daily deficit of more than 1000 calories (-2lbs per week).
This means women shouldn’t aim for lower than 1200-1500 calories per day and men no less than 1500-1800 calories per day.
If in doubt, talk to your doctor about your ideal weight and caloric goals.
How To Do Keto Math
For the sake of simplicity, we’ll walk through calculating macros for a 1500-calorie Standard Ketogenic Diet.
If math isn’t your thing, don’t worry!
Use the calculator/chart below or consult a healthcare professional. [insert table or imbed calculator? If the website doesn’t already have a macros calculator, we should program one]
Calorie goal: 1500
Macro targets: 70% fat, 20% protien, 10% carbohydrates.
Keep in mind that 1g fat = 9 calories, 1g protien = 4 calories, 1g carbs = 4 calories
To calculate how many calories should be carbohydrates, use the following formulas:
Calories from carbs: 1500 calories x 10% = 150 calories
Grams of carbs: 150 calories ÷ 4 calories/gram = 38 grams
To determine your other macros, the formula is the same:
Calories from protein: 1500 calories x 20% = 300 calories
Grams of protein: 300 calories ÷ 4 calories/gram = 38 grams
Calories from fat: 1500 calories x 70% = 1050 calories
Grams of fat: 1050 calories ÷ 9calories/gram = 117grams
Remember that these are targets and that those targets may shift with time!

Step 3: Test for Ketosis
Is your keto macro ratio working?
One of the first clues that you’re probably on the right track is a condition called keto flu.
Keto Flu
The Keto flu is a collection of symptoms you may experience as your metabolism shifts into ketosis. Symptoms include:
- Bad breath
- Brain fog
- Fatigue
- Loss of Apetite
- Nausea
- Weight loss
Most of these symptoms subside in just a week or two, at which point you should start feeling the more positive effects of ketosis. These include:
- Clearer thinking
- More energy
- Better mood
- Fewer cravings
But just feeling a certain way doesn’t mean your ketone levels are where you want them to be. The only way to know for sure is to actually measure your ketone levels.
There are several different ways to do this.
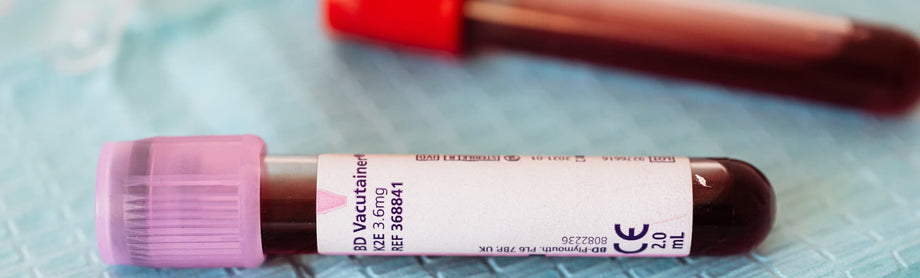
3 Ways to Test for Ketosis
The most accurate way to check your ketone levels is with a blood test, but this isn’t always practical.
Breathalyzers are being researched and may hit the market soon.
The most convenient way to check your ketone levels is with a urine test, which is available at most drug stores. [possible affiliate link?]
Conclusion: Stick With It
If you’re struggling to reach ketosis, or it’s just taking you a long time to adjust to a very low carb diet, do remember that reducing carb intake will still result in weight loss benefits, even if you don’t quite reach ketosis.
Any diet less than 150 grams of carbs per day is considered low-carb.
On a low-carb diet, insulin drops.
Insulin has many jobs, including telling fat cells to store energy and your kidneys to regulate sodium. This drop in insulin levels is also why low-carb diets help manage insulin sensitivity and diabetes.
As your carb intake decreases, you’ll likely notice that your body is shedding both excess sodium and water, reducing bloating and other signs of water retention.
This loss of water weight is one of the reasons you may see a quick drop in your body weight that then plateaus.
As great as it is to shed all that water, it’s super important that you still consume enough electrolytes like sodium. Replacing electrolytes is the best way to treat and prevent the worst effects of the keto flu.
Ketogenic diets have been demonstrated to be sustainable long-term for many patients who need them. Even folks with terminal cancer have benefited from achieving and maintaining ketosis (source).
For the average person using a ketogenic diet to lose weight, however, the extreme carb restrictions aren’t something they are prepared to sustain for life. As you reach your health and weight loss goals, carbs can be reintroduced into a balanced diet, but you’ll always want to keep your carb intake a bit lower than it probably was before your keto diet.
Whether you are starting a keto diet, are a low-carb veteran, a healthy meal delivery service can make eating keto easy so don’t forget to check out Kevin’s amazing selection of entrees and meal kits!














